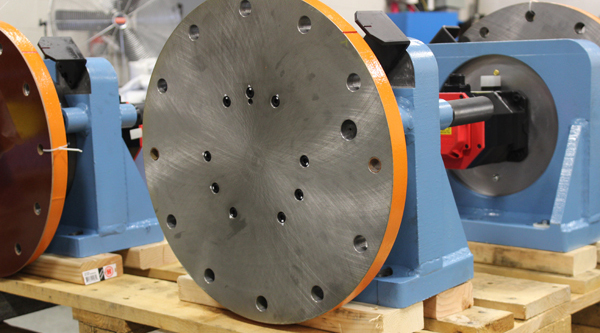
Headstock and Tailstock Considerations
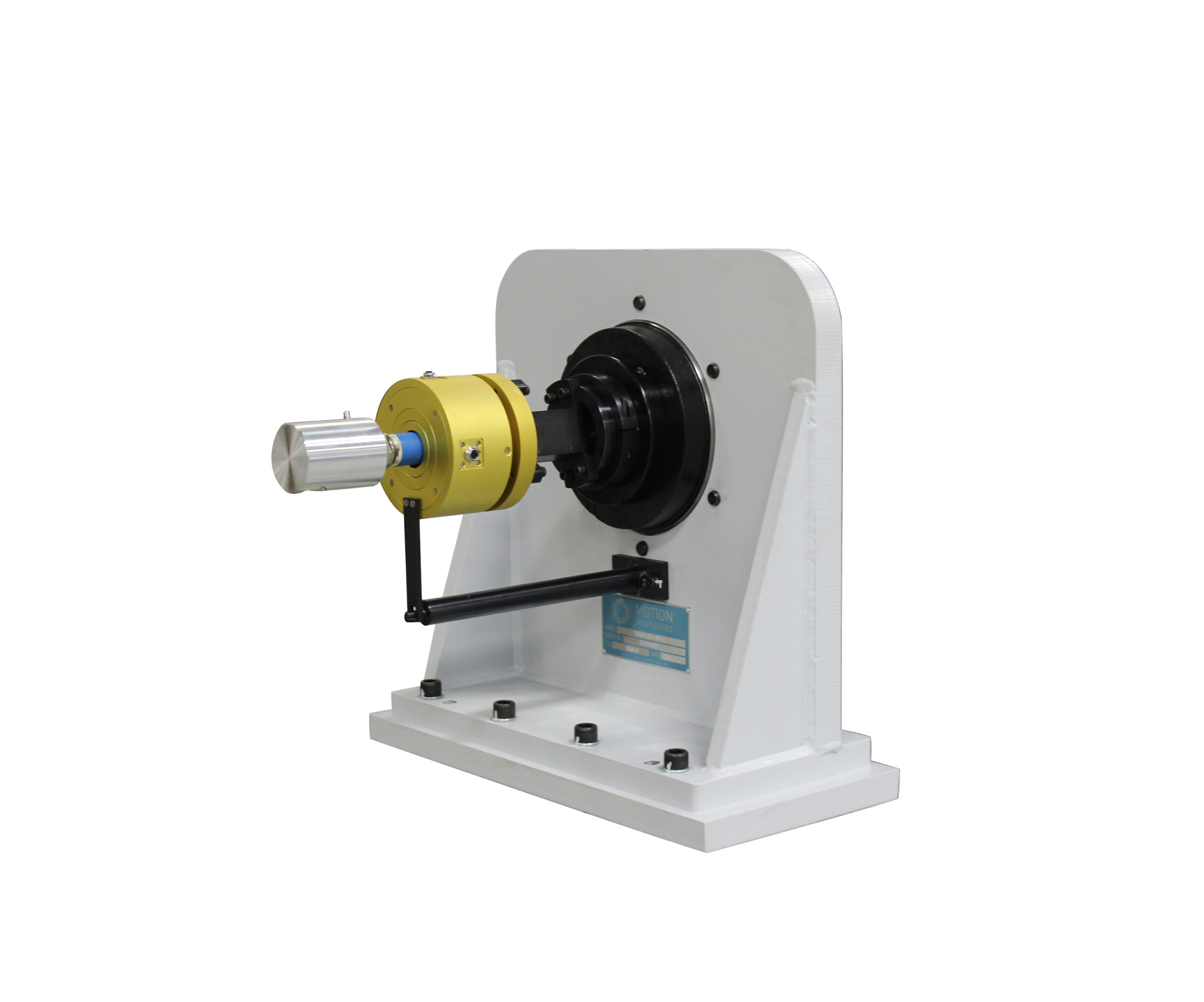
When used as a weld positioner, headstocks and tailstocks are typically oriented horizontally, with the axis of rotation parallel to the floor. This setup is designed to optimize the positioning and rotation of heavy or large workpieces during the welding or assembly process. For shorter, lighter weldments, it may be possible to use only a headstock, where the weldment is securely clamped to the rotating bed. While effective for smaller components, this setup creates an overhung load, which can lead to increased stress on the headstock and potential instability in the rotation.
For heavier or longer components, it is highly recommended to pair the headstock with a tailstock. The tailstock plays a critical role in supporting some of the weight from the overhung load, providing essential stability to prevent the workpiece from sagging or vibrating during rotation. This additional support not only enhances operational safety but also extends the longevity of the headstock by distributing the weight and reducing the wear and tear on the system. The headstock typically houses the drives, motors, and controls responsible for powering the rotational movement, while the tailstock rotates freely in sync with the headstock, maintaining workpiece alignment and stability.
For particularly heavy or large workpieces, additional support mechanisms, such as rollers or support rails, can be placed beneath the weldment to further assist with load distribution. This added support helps minimize strain on the headstock and tailstock while maintaining smooth and controlled rotation, ultimately improving the overall efficiency and safety of the welding process.
To meet specific application needs and ensure operational flexibility, the assembly system can be fully customized. Motion Index Drives offers a variety of customizable features that enhance both functionality and versatility in manufacturing environments:
- Complete assemblies
You can order fully integrated headstock-tailstock positioning systems with base frames, creating a turnkey solution for your welding or assembly processes. - Customizable mounting plate hole patterns
Both headstock and tailstock can be tailored with mounting plate hole patterns that suit your particular fixtures or tooling, ensuring seamless integration with your existing equipment. - Safety locking devices
For added safety, optional locking devices can be installed, ensuring the system remains stable during maintenance or tooling and fixture assembly. - Slip rings and rotary air unions
These optional features provide enhanced functionality, allowing for uninterrupted power and air transfer to rotating parts, critical for certain welding or assembly applications.
View more information on Headstock Tailstock positioners.